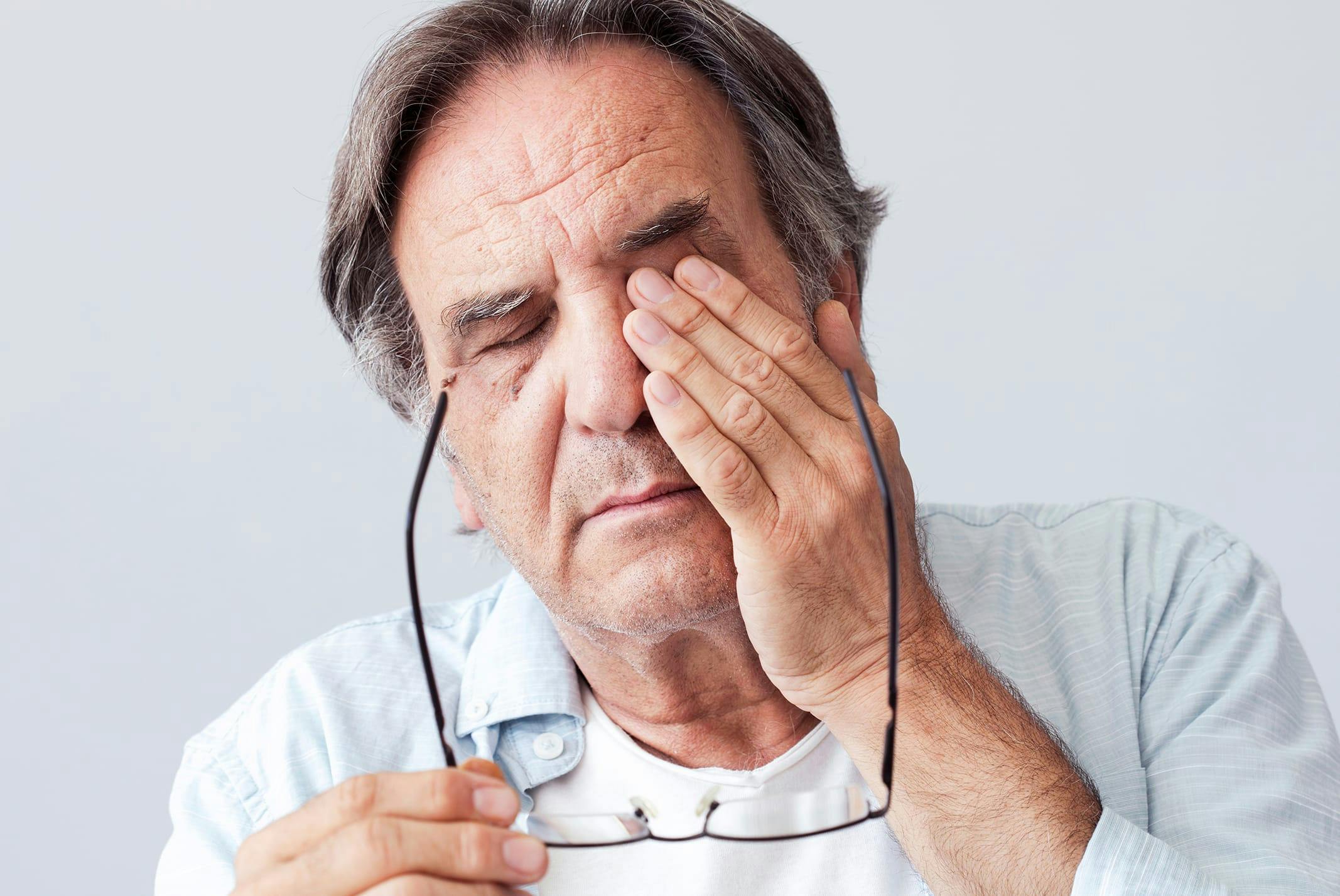
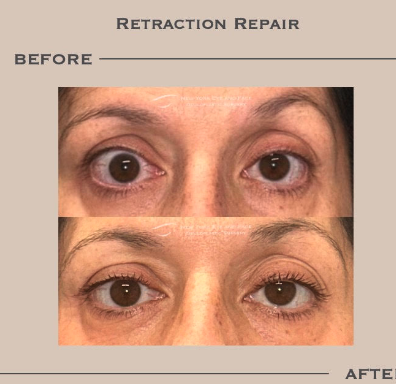
Eyelid retraction occurs when the eyelid is pulled abnormally high, exposing the white of the eye above or below the colored part, known as the iris. If you're experiencing difficulty closing your eyes or discomfort due to retracted eyelids, you're likely aware of the strain it can put on your eye health and appearance.
Causes of Eyelid Retraction
Thyroid Eye Disease
Thyroid eye disease is a complex condition that can significantly impact the eyes and surrounding structures. It is primarily associated with Graves' disease, an autoimmune disorder characterized by an overactive thyroid gland. However, thyroid eye disease can also occur in those with other thyroid disorders or even in the absence of thyroid dysfunction.
Here’s what you need to know:
- The underlying mechanism of thyroid eye disease involves the immune system mistakenly attacking tissues around the eyes
- This autoimmune response targets specific proteins within the orbital tissues, including muscles, fat, and connective tissue
- The immune-mediated inflammation leads to swelling, scarring, and fibrosis in the affected tissues
One of the hallmark features of thyroid eye disease is eyelid retraction, where the upper and/or lower eyelids are positioned higher than usual. This can create a wide-eyed or staring appearance, often described as "lid lag" or "staring eyes." The retraction occurs due to the inflammation and scarring affecting the muscles and connective tissue that control eyelid movement.